_______________________
1. DNS Lowndown
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system built on a distributed database for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. Most importantly, it translates domain names meaningful to humans into the numerical identifiers associated with networking equipment for the purpose of locating and addressing these devices worldwide.
An often-used analogy to explain the Domain Name System is that it serves as the phone book for the Internet by translating human-friendly computer hostnames into IP addresses. For example, the domain name www.example.com translates to the addresses 192.0.32.10 (IPv4) and 2620:0:2d0:200::10 (IPv6).
The Domain Name System makes it possible to assign domain names to groups of Internet resources and users in a meaningful way, independent of each entity's physical location. Because of this, World Wide Web (WWW) hyperlinks and Internet contact information can remain consistent and constant even if the current Internet routing arrangements change or the participant uses a mobile device. Internet domain names are easier to remember than IP addresses such as 208.77.188.166 (IPv4) or 2001:db8:1f70::999:de8:7648:6e8 (IPv6). Users take advantage of this when they recite meaningful Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) and e-mail addresses without having to know how the computer actually locates them.
_______________________
_______________________
3. How Malware Works
Malware, short for malicious software, (sometimes referred to as pestware) is a software designed to harm or secretly access a computer system without the owner's informed consent. The expression is a general term used by computer professionals to mean a variety of forms of hostile, intrusive, or annoying software or program code. Click on the link below:
Software is considered to be malware based on the perceived intent of the creator rather than any particular features. Malware includes computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, spyware, dishonest adware, scareware, crimeware, most rootkits, and other malicious and unwanted software or program. In law, malware is sometimes known as a computer contaminant, for instance in the legal codes of several U.S. states, including California and West Virginia.
Preliminary results from Symantec published in 2008 suggested that "the release rate of malicious code and other unwanted programs may be exceeding that of legitimate software applications."[6] According to F-Secure, "As much malware [was] produced in 2007 as in the previous 20 years altogether." Malware's most common pathway from criminals to users is through the Internet: primarily by e-mail and the World Wide Web.
_______________________
4. Credit Card Codes
_______________________
5. Leaving Facebook Comments
_______________________
6. Take the Arial/Helvetica Quiz
_______________________
7. Apple Escapades
_______________________
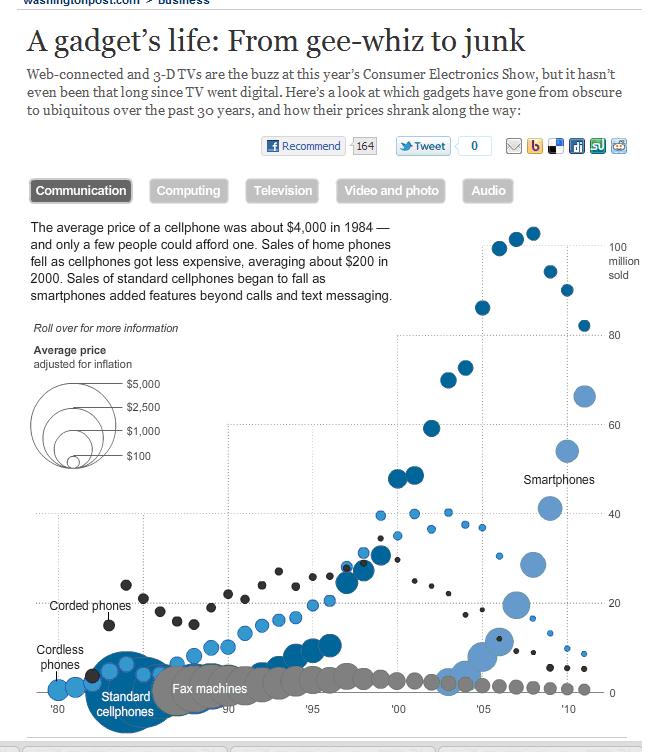
8. Gadget Lifecycles
Web-connected and 3-D TVs are the buzz at this year’s Consumer Electronics Show, but it hasn’t even been that long since TV went digital. Here’s a look at which gadgets have gone from obscure to ubiquitous over the past 30 years, and how their prices shrank along the way:
Have a look at the interactive graphic at the link below:
_______________________
_______________________
11. Creativity Infographic
_______________________
12. HTML Quizzes
Panic. I have 2 Quizzes for you to do today to review your knowledge. You should be able to tackle these with ease now, do the questions then let me know your final score:
No. 1www.w3schools.com/html/html_quiz.asp
No.2








1 comment:
wow awesome Pict. of evil furniture!!
Post a Comment