_______________________
1. A Look at Internet Hardware
Its worth remembering that for all its power, the Internet is a series of networks based on primarily copper cabling and today, more crucially, fibre optic cables:
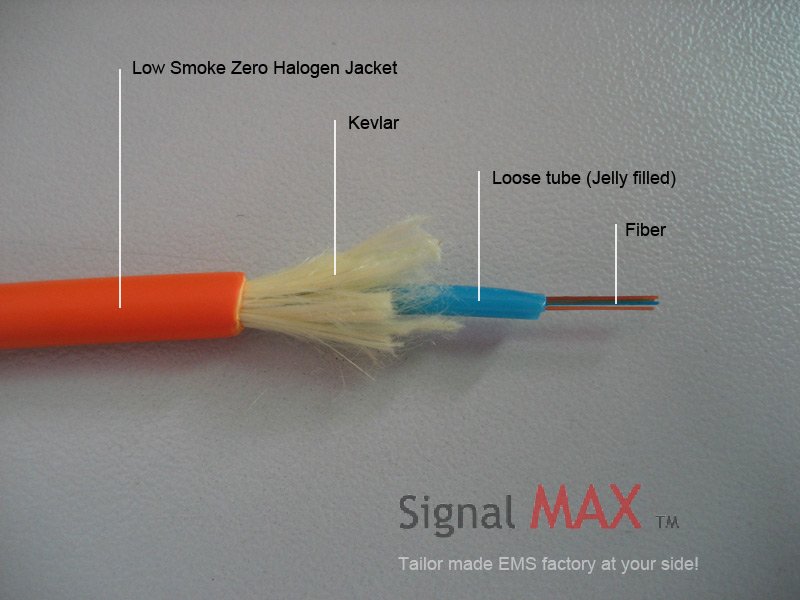
The traditional method of data transmission over copper cables is accomplished by transmitting electrons over a copper conductor. Fiber Optic cables transmit a digital signal via pulses of light through a very thin strand of glass. Fiber strands (the core of the fiber optic cable) are extremely thin, no thicker than a human hair. The core is surrounded by a cladding which reflects the light back into the core and eliminates light from escaping the cable.
A fiber optic chain works in the following manner. At the one end, the fiber cable is connected to a transmitter. The transmitter converts electronic pulses into light pulses and sends the optical signal through the fiber cable. At the other end, the fiber cable is plugged into a receiver which decodes the optical signal back into digital pulses.
Multimode vs Singlemode Fiber
A "mode" in Fiber Optic cable refers to the path in which light travels. Multimode cables have a larger core diameter than that of singlemode cables. This larger core diameter allows multiple pathways and several wavelengths of light to be transmitted. Singlemode cables have a smaller core diameter and only allow a single wavelength and pathway for light to travel.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Fiber Optic cable
There are many advantages and disadvantages in using fiber optic cable instead of copper cable. One advantage is that fiber cables support longer cable runs than copper. In addition, data is transmitted at greater speeds and higher bandwidths than over copper cables.
There are many advantages and disadvantages in using fiber optic cable instead of copper cable. One advantage is that fiber cables support longer cable runs than copper. In addition, data is transmitted at greater speeds and higher bandwidths than over copper cables.
The major disadvantages of fiber optic cables are cost and durability. Fiber cables are more expensive than copper cables and much more delicate.
...................................
Australia's NBN
The NBN is one of the largest (and most disputed) public infrastructure currently under in OECD countries and indeed the world. Australia is seeking the overcome the tyranny of distance with a high-speed fibre-optic network.
National Broadband Network (NBN) is a open access telecommunication network under construction to overcome the digital divide in Australia. Fibre to the premises (FTTP) will provide up to one gigabit per second to 93% of Australians, with the remaining premises serviced by fixed wireless and satellite technologies with a minimum speed of twelve megabits per second. The NBN, the largest single infrastructure investment in Australia's history, was announced after the Request for Proposals (RFPs) for the original A$4.7 billion election promised NBN was terminated by then Prime Minister Kevin Rudd, after facing a large compensation payment to Telstra and being unable to find private sector funding during the global financial crisis. Following the revised Tasmanian Government's proposal, the Tasmania rollout began in July 2009 with the first services going live in July 2010.
The NBN will have committed download speeds of one hundred megabits per second with peak speed of one gigabit per second for 93% of Australian connected via FTTH using a Gigabit Passive optical network (GPON) or Ethernet Point-to-Point fibre, while the remainder will be serviced by fixed wireless and satellite technologies with a minimum speed of twelve megabits per second.
The IT industry initially kept a neutral to positive opinion of the NBN, however with few exceptions are now supportive of the NBN.
Peak Australian business group, the Australian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (ACCI) support the NBN with the CEO Peter Anderson calling it a "real productivity kick and benefit", but also called for more openness in relation to the costs of the project.
Homes and businesses are connected to a Point of Interconnect (PoI) via GPON, Ethernet, fixed wireless or satellite. Businesses within the 93% fibre footprint can be connected using Ethernet while home users will be connected via GPON. Homes and businesses outside the fibre footprint will be connected via fixed wireless or satellite. The fibre, fixed wireless or satellite will be connected to a Network Termination Unit (NTU) which gives four Ethernet ports and two Analogue Telephone Adapters (ATA).
The original NBN was an election promise by then opposition leader Kevin Rudd leading up to the 2007 Australian Federal Election. The plan was to build a A$15 billion fibre to the node (FTTN) network with the co-operation of the private sector, including a government contribution of A$4.7 billion. This would end the conflict of interest of Telstra wholesaling Australia's major telecommunications infrastructure, known as the copper network, and also providing retail services.
.......................................
Have a go at these Home Networking Quizzes and test your knowledge of networking basics:
_______________________
2. Web Fundamentals Chapter Three
_______________________
2. Web Fundamentals Chapter Three
Work through Chapter Three of the Web Fundamentals course, we will do a brief quiz on the Web Fundamentals that covers this content today.
3. Being a Successful Apple is hard
Apple are not happy that everyone wants to make products like theirs. They are crying foul. One such offending object is the Zoom Android Tablet:
http://www.smh.com.au/digital-life/tablets/xoom-launch-begins-android-tablet-onslaught-as-apple-takes-gloves-off-20110419-1dm6e.html
http://www.smh.com.au/digital-life/tablets/xoom-launch-begins-android-tablet-onslaught-as-apple-takes-gloves-off-20110419-1dm6e.html
Too Applely?
_______________________
4. Life Online
4. Life Online





















1 comment:
After reading the timeline, i find it quite interesting to think of the future in such long terms, it is actually very exciting taking in consideration that we don't really know whats going to happen, vey interesting and funny at some ponts ::)
Post a Comment